LeanSentry monitors your servers by using standard Windows management protocols, and accessing them either locally (when you install LeanSentry on each server using the Local option) or remotely (when you install using the Remote option).
In some environments, a variety of reasons can cause LeanSentry to fail to connect to your servers, in which case it will show you a warning in the dashboard and report an error on your environment configuration page.
This article will help you troubleshoot the common problems quickly and get back to monitoring your app.
NOTE: If you're having problems on Amazon EC2, skip to step 5. NetBIOS was disabled by default in the new Windows Server AMIs provided by AWS.
1. Review the cause of connectivity problems
First, find the server that is having the problem on your environment configuration page:

Click the error link to view its details. In many cases, LeanSentry will automatically perform a network diagnostic to determine the likely reason for connectivity problems, and suggest next steps for you to try.

2. Resolve the connectivity problem
Here are the most common problems, and how to solve them:
1. Incorrect server hostname.
This is the most likely cause of connectivity problems. Double-check that the server name is a valid internal DNS or netbios hostname for the server, that the Monitoring service can use to connect to the server internally. Do not use a public domain name.
In this case, the network diagnostic will typically report a DNS resolution failure, or the inability to PING the specified hostname.
2. No network connectivity to server.
The Monitoring service must have network connectivity to the server being monitored. Ideally, this means that the server should be on the same internal network as the Monitoring service.
In this case, the network diagnostic will typically report a DNS resolution failure, or the inability to PING the specified hostname.
3. Firewall rules prevent network connectivity to required ports.
The Monitoring service requires that several system ports be opened between the machine where the Monitoring service is installed, and the server being monitored. In the Remote deployment model, make sure to run the appropriate prepserver.bat file on each server being monitored (this will open the required ports in the server's Windows Firewall).
Notes:
- If the Monitoring service and the server being monitored ARE NOT in the same subnet, make sure to use the no-subnet version of prepserver.bat. In this case, you must have an external firewall protecting your network from unauthorized access to the opened ports.
- If you have an intermediate network firewall between the Monitoring service and the monitored server, be sure to create exceptions to allow the Monitoring service to connect to these ports. A common example of this is Amazon EC2, where the Monitored service and the server are in two separate security groups. See the prepserver option table for the list of ports to open.
WARNING: DO NOT open the ports to the internet! LeanSentry does not connect to your environment from the outside. The ports should only be opened between the Monitoring service and the monitored servers, both located inside your environment.
4. Windows management protocols are not listening on the IP address to which the Monitoring service is connecting.
This is a rare case, but it does happen occasionally whenever the server being monitored has multiple network interfaces (NICs) or IP addresses bound to its network interfaces.
In this case, the Monitoring service may chose one of the IP addresses that does not have the Windows management protocols listening on it.
The network diagnostic will show all the IP addresses to which the server hostname resolves.
If you suspect this is the issue, you can try the following:
1. Remove the server, and re-add it with a different IP address.
2. Run the following command on the server:
netstat /a /p tcp | findstr /i /c:139
This command will print out the IP addresses that may be used to connect to the server.
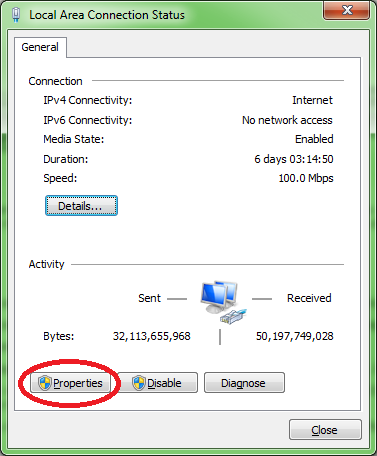
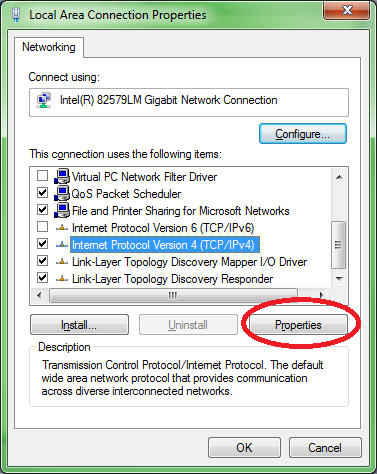
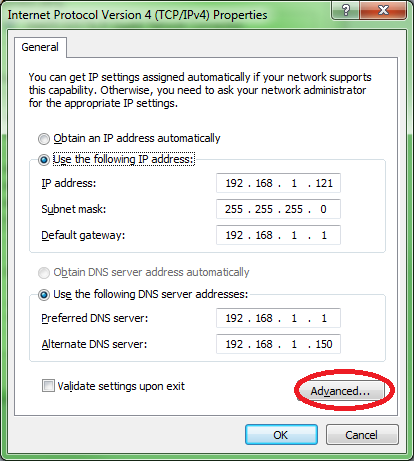
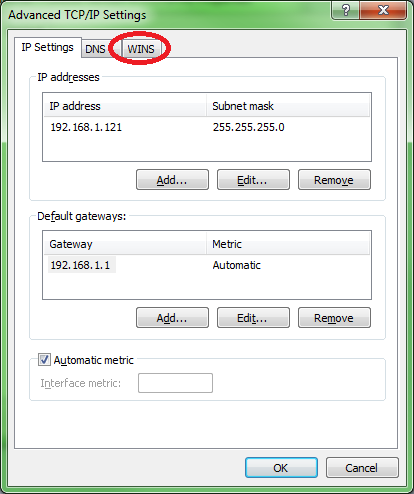
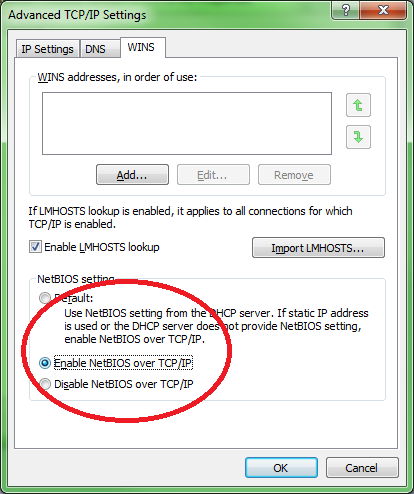
5. Make sure NetBios over TCP/IP is enabled on the server's network adapter
Make sure that NetBIOS over TCP/IP is enabled on the network adapter to which LeanSentry is connecting.
Here are the steps to check:
6. If your server CPU is heavily overloaded, LeanSentry may fail to connect to the server.
In this case, LeanSentry may time out while trying to connect to the server, and report an error stating:
"Failed to obtain data from the performance counter provider"
To verify that LeanSentry can connect, open PerfMon on the monitoring service machine, and attempt to add the "Processor\% Processor Time" counter for the remote server by specifying its name like \\mysrv1. If you receive an error, this indicates that there is a connection problem that needs to be addressed before LeanSentry would be able to connect.
One option is to log in to the machine you're trying to monitor and find the process that is consuming most of the CPU time. You can lower the process scheduling priority through the task manager:

This should cause the process to give enough CPU cycles to allow LeanSentry to connect.
If you find that a website is the culprit that's pegging the CPU, you can also limit its application pool's CPU usage. See http://www.iis.net/learn/manage/managing-performance-settings/using-wsrm-to-manage-iis-7-apppool-cpu-utilization for instructions on how to do this.
If you have any other questions, or are still having trouble getting LeanSentry to connect to your servers, please email us!

Comments
0 comments
Article is closed for comments.